React架构之Render阶段上(beginWork)
从架构了解React Render阶段的流程,本篇文章主要从"递"阶段beginWork来展开,设计到Reconciler相关内容。
Render阶段概览
我们知道 Fiber Reconciler 是从** Stack Reconciler 重构而来,通过遍历的方式实现可中断的递归,所以Render可以分为 "递"和"归"**两部分。
"递"阶段(生成Fiber树的过程)
首先从 rootFiber 开始向下深度优先遍历。为遍历到的每个 Fiber节点 调用 beginWork 方法。
改方法会根据传入的Fiber节点创建子Fiber节点,并将这两个Fiber节点链接起来。
当遍历到叶子节点(即没有子组件的组件)时,就会进入"归"阶段。
"归阶段"(生成或更新DOM节点、收集effectList)
在"归阶段"会调用 completeWork ,如果其存在兄弟Fiber节点(即fiber.sibling !== null ),会进入其兄弟Fiber的"递"阶段。
如果不存在 兄弟Fiber,会进入父级Fiber的"归"阶段。
"递"和"归"阶段会交错执行到"归"到 rootFiber。至此,render阶段的工作就结束了。
方法概览
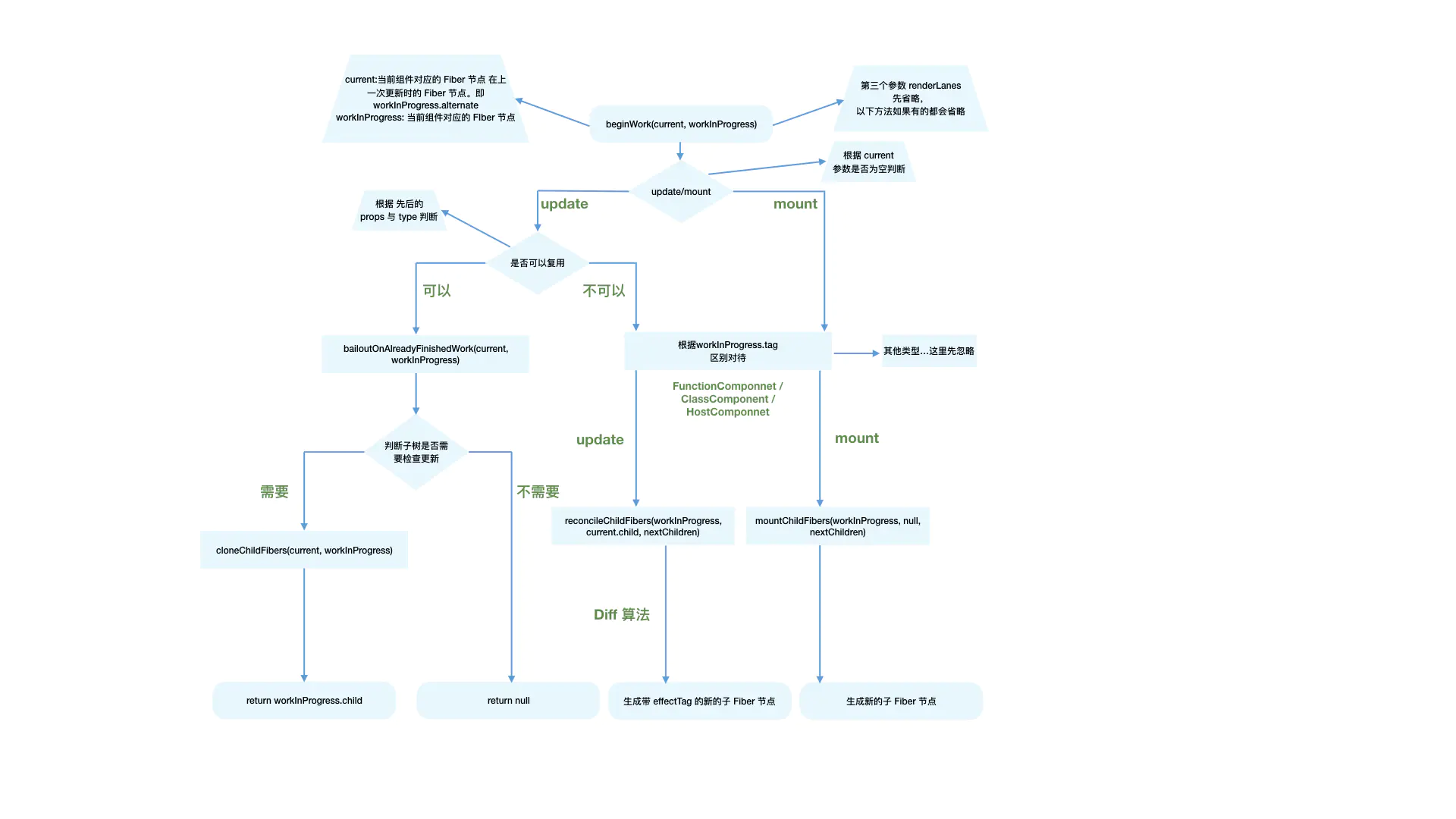
beginWork 的工作是传入 当前Fiber节点,创建 子Fiber节点。
从传参看方法执行
已複製!function beginWork( current: Fiber | null, workInProgress: Fiber, renderLanes: Lanes, ): Fiber | null { // ...省略函数体 }
各参数含义:
- current:当前组组件对应的 FIber节点 在上一次更新时的 Fiber节点,即workInProgress.alternate
- workInProgress: 当前组件对应的Fiber节点
- renderLanes: 优先级相关
我们知道除了 rootFiber 以外,组件 mount 时,由于是首次渲染,是不存在当前组件对应的 Fiber节点 在上一次更新时的 Fiber节点,即 mount 时 current === null 。
组件 update 时,由于之前已经 mount 过,所以 current !== null 。
所以我们可以通过 current === null ? 来区分组件是处于mount 还是 update 。
也正是因为这个原因,beginWork 的工作可以分为两个部分:
- update 时,如果 current 存在,在满足一定条件时可以复用 current 节点,这样就能克隆 current.child 作为 workInProgress.child ,而不需要新建 wordInProgress.child,这也就是Reconcile 中 Diff算的作用。
- mount 时,除 fiberRootNode 以外,current === null 。会根据fiber.tag 的不同来创建不同类型的子Fiber节点。
已複製!function beginWork( current: Fiber | null, workInProgress: Fiber, renderLanes: Lanes ): Fiber | null { // update时 if (current !== null) { // ...省略 // 如果current存在可能存在优化路径,可以复用current(即上一次更新的Fiber节点) // bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork 命中了优化方法 return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork( current, workInProgress, renderLanes, ); } else { didReceiveUpdate = false; } // mount时:根据tag不同,创建不同的子Fiber节点 switch (workInProgress.tag) { case IndeterminateComponent: // ...省略 case LazyComponent: // ...省略 case FunctionComponent: // ...省略 case ClassComponent: // ...省略 case HostRoot: // ...省略 case HostComponent: // ...省略 case HostText: // ...省略 // ...省略其他类型 } }
mount时
首次渲染或者不满足优化路径时,创建 子Fiber 。
根据 fiber.tag 的不同,进入不同类型的 FIber 的创建逻辑。
可以从这里看到 tag 对应的续件类型
已複製!// mount时:根据tag不同,创建不同的Fiber节点 switch (workInProgress.tag) { case IndeterminateComponent: // ...省略 case LazyComponent: // ...省略 case FunctionComponent: // ...省略 case ClassComponent: // ...省略 case HostRoot: // ...省略 case HostComponent: // ...省略 case HostText: // ...省略 // ...省略其他类型 }
对于我们常见的组件类型,如( FunctionComponent / ClassComponent / HostComponent ),最终会进入 reconcileChildren 方法。
update时
满足以下情况时 didReceiveUpdate === false (即可以直接复用前一次更新的 子Fiber,不需要新建 子Fiber )
- oldProps === newProps && workInProgress.type === current.type ,即 props 与 fiber.type 不变。
- !includesSomeLane(renderLanes, updateLanes),即当前 Fiber节点 优先级不够。
已複製!// current !== null 即 update 阶段 if (current !== null) { const oldProps = current.memoizedProps; const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps; if ( oldProps !== newProps || hasLegacyContextChanged() || (__DEV__ ? workInProgress.type !== current.type : false) ) { // 组件有更新 didReceiveUpdate = true; } else if (!includesSomeLane(renderLanes, updateLanes)) { // 组件优先级不够 didReceiveUpdate = false; // 省略处理 // 命中优化, 最终执行cloneChildFibers复用 return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(current, workInProgress, renderLanes); } else { didReceiveUpdate = false; } } else { didReceiveUpdate = false; }
reconcileChildren
从函数名也可以看出来这是 Reconciler 模块的互信部分。它的作用如下:
- 对于 mount 的组件,他会创建新的 子Fiber节点
- 对于 update 的组件,他会将唐倩组件与该组件在上次更新是对应的 Fiber节点 比较(也就是俗称的Diff算法),将比较更新的结果生成新 Fiber节点
已複製!export function reconcileChildren( current: Fiber | null, workInProgress: Fiber, nextChildren: any, renderLanes: Lanes ) { if (current === null) { // 对于mount的组件, // 执行mountChildFibers workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers( workInProgress, null, nextChildren, renderLanes, ); } else { // 对于update的组件 // 执行reconcileChildFibers workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers( workInProgress, current.child, nextChildren, renderLanes, ); } } // 在ReactChildFiber.old.js中 // 传入了不同的布尔值 // 判断是否追踪副作用 export const reconcileChildFibers = ChildReconciler(true); export const mountChildFibers = ChildReconciler(false);
从 mountChildFibers 和 reconcileChildFibers 两个方法中可以看出,同 beginWork 一样,也是通过current === null ? 来区分 mount 与 update。
不论走哪个逻辑,最终都会生成新的 子Fiber节点 并赋值给 workInProgress.child,作为本次 beginWork 返回值。
注意 mountChildFibers 与 reconcileChildFibers 这两个方法的逻辑基本一致,唯一的区别就是传入的布尔值,当布尔值为true即调用的是reconcileChildFibers 会为生成的Fiber节点带上effectTag属性,而mountChildFiber不会。
思考问题 :(fiber.effectTag & Placement)!== 0 ,即 Fiber节点 存在 Placement effectTag 我们知道, mount 时,fiber.stateNode === null ,且在 reconcileChildren 中调用的 mountChildFibers 不会为 Fiber节点 赋值 effectTag。那么首屏渲染是如何完成?
假设 mountChildFibers 也会赋值 effectTag,那么可以遇见 mount 时,整棵 Fiber树 所有节点都会有 Placement effectTag。那么 commit阶段 在执行 DOM 操作是每个节点都会执行一次插入操作,这样大量的 DOM 操作是非常低效的。
为了解决这个问题,在 mount 时只有 rootFiber 会赋值 Placement effectTag,在commit 只有执行一次插入操作。这个有点像在js中动态渲染多条数据的问题,解决方案有标准的DOM方法和使用innerHTML两种。
已複製!// 标准的DOM方法 ,通过appendChild实现 // 每次循环都要重新渲染 // 数据量越大、耗时越久 var frag = document.createDocumentFragment(); for (var i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { var el = document.createElement('p'); el.innerHTML = i; frag.appendChild(el); } document.body.appendChild(frag); // 可以替换为:innerHTML方法 // 用字符串保存DOM数据,最后一次渲染 var html = []; for (var i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { html.push('<p>' + i + '</p>'); } document.body.innerHTML = html.join('');
参考资料