CSS Position 属性
在你真正擅长CSS之前,你需要了解基础知识。您必须了解 CSS 属性及其值
现代前端框架的工作原理
这个问题来源于最近的一道面试题,过程中只是说了一个大概,在这篇文章中,我们将重点介绍 CSS position 属性。我们将学习 CSS position 属性的各种值以及它们的工作原理。让我们开始吧!
CSS position 属性定义元素在文档中的位置。此属性与 left、right、top、bottom 和 z-index 属性一起使用,以确定元素在页面上的最终位置。
position 属性可以采用五个值。它们是:
- static
- relative
- absolute
- fixed
- sticky
1.Static
这是元素的默认值。元素根据文档的正常流程进行定位。left 、right 、top 、bottom 和 z-index 属性不会影响position:static 的元素。
让我们用一个例子来说明这个position:static对元素的位置没有影响。我们在父容器中放置了三个 div。我们将在整篇文章中使用此示例。
已複製!<html> <body> <div class="parent-element"> <div class="sibling-element">I'm the other sibling element.</div> <div class="main-element">All eyes on me. I am the main element.</div> <div class="sibling-element">I'm the other sibling element.</div> </div> </body> <html> <style> .main-element { position: static; left: 10px; bottom: 10px; background-color: yellow; padding: 10px; } .sibling-element { padding: 10px; background-color: #f2f2f2; } </style> </html> </html>
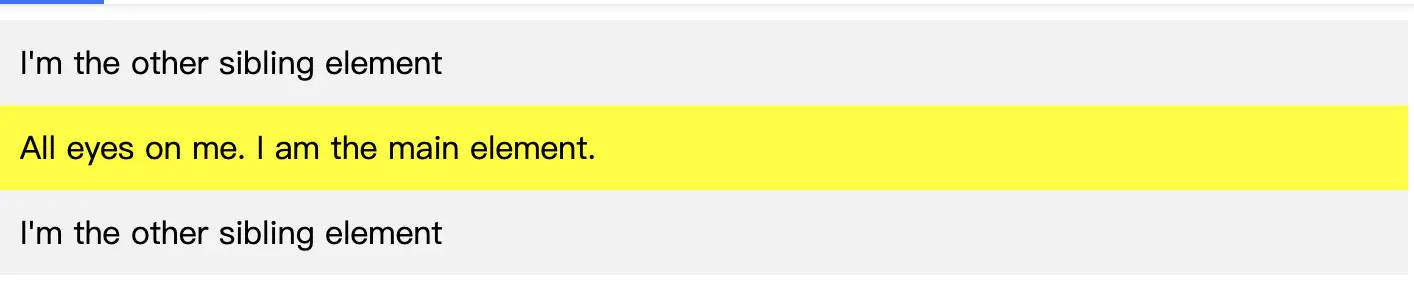
.main-element 布局没有发生变化,这证实了 left 和 bottom 属性不会影响 position: static 的元素。
2.Relative
position:relative 的元素保留在文档的正常流程中。但是,与静态元素不同,left、right、top、bottom 和 z-index 属性会影响元素的位置。基于左、右、上和下属性值的偏移量应用于元素相对于自身。
我们将上述的样式修改一下:
已複製!.main-element { position: relative; left: 10px; bottom: 10px; background-color: yellow; padding: 10px; }
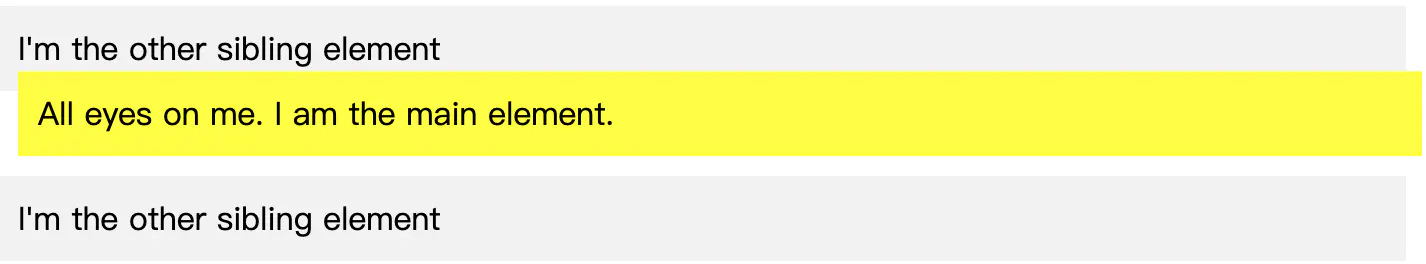
请注意,left 和 bottom 属性现在会影响元素的位置。
另请注意 ,该元素 仍保留在文档的正常流程中,并且相对于其自身应用偏移量。当我们继续讨论其他值时,请注意这一点。
3.Absolute
position: absolute 的元素相对于其父元素进行定位。在这种情况下,将从正常文档流中删除该元素。其他元素的行为就像该元素不在文档中一样。不会在页面布局中为元素创建任何空间。left、top、bottom 和 right 的值决定了元素的最终位置。
需要注意的一点是,具有 position: absolute 的元素相对于其最接近的祖先定位。这意味着父元素必须具有 position: static 以外的 position 值。
如果最近的父元素未定位,则该元素相对于定位的下一个父元素进行定位。如果没有定位的祖先元素,则它是相对于 <html> 元素定位的。
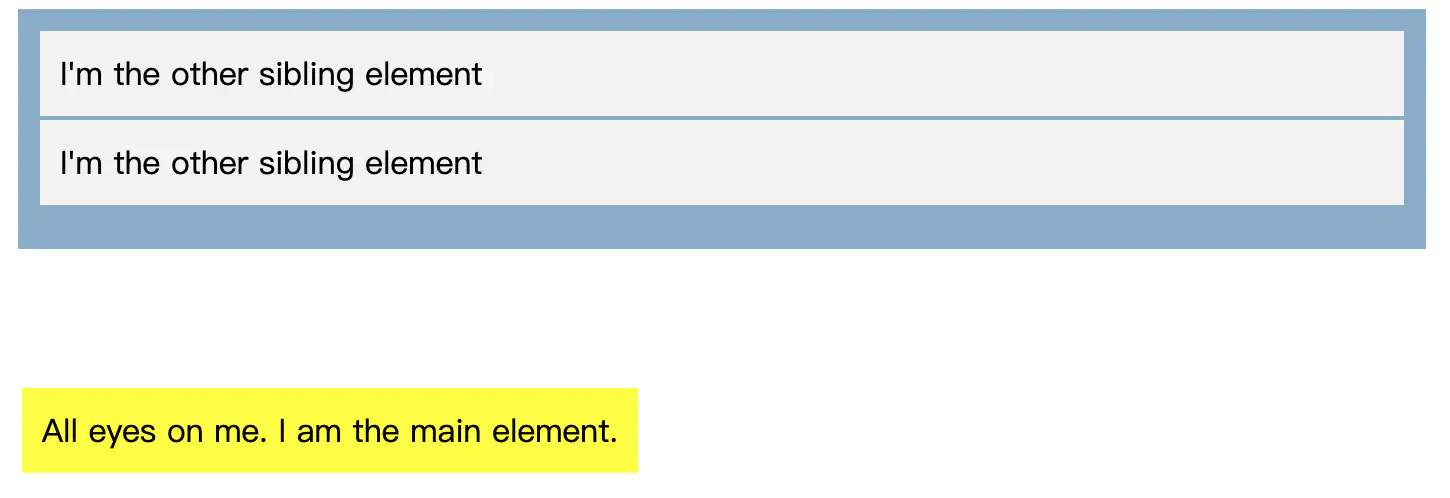
在这种情况下,我们将主元素的位置更改为位置:绝对。我们还将为其父元素提供一个相对位置,以便它不会相对于 <html> 元素进行定位。
已複製!.main-element { position: absolute; left: 10px; bottom: 10px; background-color: yellow; padding: 10px; } .parent-element { position: relative; height: 100px; padding: 10px; background-color: #81adc8; } .sibling-element { background: #f2f2f2; padding: 10px; border: 1px solid #81adc8; }

请注意 ,文档中没有为该元素创建空格。该元素现在相对于父元素进行定位。当我们继续下一个值时,请注意这一点。
4.Fixed
固定位置元素类似于绝对定位元素。它们也会从文档的正常流程中删除。但与绝对定位的元素不同,它们始终相对于 <html> 元素定位。
需要注意的一点是, 固定元素不受滚动的影响 。它们始终保持在屏幕上的相同位置。
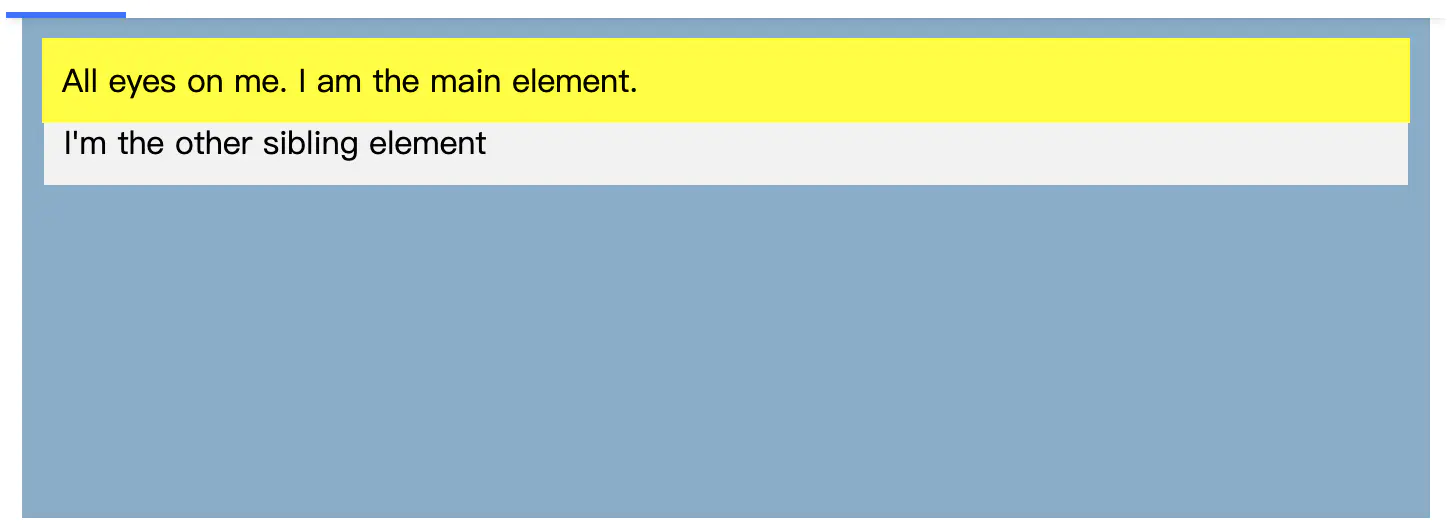
已複製!.main-element { position: fixed; bottom: 10px; left: 10px; background-color: yellow; padding: 10px; } html { height: 800px; }
在这种情况下,元素相对于 <html> 元素进行定位。尝试滚动以查看该元素是否已固定在屏幕上。
5.Sticky
position:sticky 是 position:relative 和 position:fixed 的混合。它就像一个相对定位的元素,直到某个滚动点,然后它就像一个固定的元素。如果您不明白这意味着什么,请不要害怕,这个例子将帮助您更好地理解它。
已複製!.main-element { position: sticky; top: 10px; background-color: yellow; padding: 10px; } .parent-element { position: relative; height: 800px; padding: 50px 10px; background-color: #81adc8; }

滚动结果选项卡以查看结果。你会看到它作为一个相对元素,直到它到达屏幕上的某个点,顶部:10px,然后它就像一个固定元素一样到达那里。